Tired of scouring countless resumes looking for that ‘ideal candidate’? We get you.
With thousands of applications pouring in for every open position, finding the right candidate can feel like searching for a needle in a haystack. But what if there was an efficient way to narrow down your search?
Enter Boolean search—a game-changing technique that gives you precision in your recruitment process.
Boolean search allows you to use simple, powerful operators to filter through resumes, job boards, and LinkedIn profiles with incredible accuracy. By combining keywords with operators like AND, OR, NOT, and parentheses, you can create highly targeted search queries that zero in on exactly the qualifications, skills, and experience you need.
For example, if you’re searching for a software engineer with experience in both Java and Python, you can use:
("Java" AND "Python" AND "Software Engineer")
Need to exclude candidates who don’t have a degree? You can use:
("Java" AND "Python" AND "Software Engineer" NOT "Associate Degree")
With Boolean search, you can quickly filter resumes, narrowing down your list to only the best candidates.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll walk you through how to use boolean search in recruitment in 2026, the most common operators, and advanced techniques to help you streamline your recruiting process and save valuable time.

What is Boolean Search, and How Does This Concern HRs?
Boolean search is a powerful search technique based on the principles of Boolean logic. It uses a combination of keywords and operators like AND, OR, and NOT to limit or broaden search results. Developed by 19th-century mathematician George Boole, this technique uses specific relationships between elements to deliver precise search results.
For HR professionals, Boolean search is a silver lining in the complex recruitment process as it can narrow down vast databases of resumes by filtering out irrelevant results. It only highlights those profiles that meet specific criteria, saving time, reducing frustration, and increasing the chances of making the right hire.
What are the Basic Boolean Search Operators?
Here are the three basic Boolean search operators that are widely used in the recruitment space:

AND Operator
This operator narrows your search results by including multiple criteria. When you use AND between two or more keywords, the search engine will return results that contain all of the specified keywords. This ensures that only candidates or profiles that match both (or all) criteria are included.
For example, if you are looking only for content marketers, simply search for “Content AND Marketer.” This will return profiles with both Content and marketer in the resume or profile and eliminate other types of marketers, like product marketers or affiliate marketers.

OR Operator
The OR operator broadens your search by allowing the input of multiple possible keywords. When you use OR between terms, the search engine will return results that include either of the specified terms. This is useful when different terms or synonyms could apply to your search.
For example, if you are looking for a developer, you can use “Developer OR Programmer”. This will show results containing either developer or programmer, ensuring that you don’t miss out on candidates who may use one title over the other but possess similar skills.

NOT Operator
The NOT operator helps you exclude certain terms from your search results. This is particularly useful when you want to filter out candidates who might not meet certain qualifications, or they are in a different field than you’re targeting.
For example, if you are looking for a mid-level developer, you can search using the phrase “Developer NOT Junior”. This will return profiles of developers but exclude those who are labeled as junior or avoid entry-level candidates.

Advanced Boolean Search Operators
While the basic operators are sufficient for very simple operations, you cannot use them for complex search queries. To help you with that, there are certain advanced Boolean search operators that are used in conjunction with the basic operators.

() (Parentheses)
It is used to group keywords and operators. It is typically used for more complex and structured searches. For example, use “(engineer AND (Python OR Java))” to find profiles of engineers who know either Python or Java.
“” (Quotation Marks)
They are used to search for an exact phrase. When you enclose a phrase in quotes, the search engine will return results that include that exact phrase in the exact same order. For example, if you use the phrase “project manager”, it will return only results that contain the exact phrase project manager. It will filter out results with either word appearing separately or in a different order. Even results containing ‘manager project’ will be rejected.
site:
This operator allows you to search within a specific website. This is especially useful when looking for candidate profiles or information from particular sites like LinkedIn. For example, when you use site:linkedin.com “Account Manager”, it will return results specifically from LinkedIn that contain the above phrase.
Pro Tip: If you want to see only LinkedIn profiles that match your string and exclude other content, such as posts or articles, add a /in/ to the string. In the above example, use site: linkedin.com/in/ “Account Manager”, instead.
filetype:
This advanced operator narrows search results to specific file types. It could be PDFs, Word documents, or Excel files. This is particularly useful for finding resumes in a particular format. For example, you can use – filetype:pdf(resume OR CV) AND “Data Scientist” to find a data scientist in your database who has uploaded a resume in the PDF format.
*** (Asterisk)
This operator allows you to search for variations of a word. It can replace part of a word or serve as a placeholder for unknown terms. It minimizes the risk of missing good candidates just because the candidates described their roles, experience or skills using different versions of the phrase. For example, if you use market**, the query will return results containing market, marketer, marketing, and so on.
inurl:
This operator finds web pages that contain specific keywords in the URL. It is particularly useful for finding profiles on websites other than LinkedIn such as a personal blog. Searching for Inurl:blog “C++ Programmer” will return profiles of C++ programmers who have a blog.
AROUND(n)
It comes up with results where two keywords appear within the mentioned number of words from each other. It gives you more control over contextual relevance. For example, when you use Business Analyst AROUND(4) Requirements, you will get results where the terms Business Analyst and Requirements are within four words of each other, ensuring they are mentioned in a relevant context.
NEAR Operator
This operator works similarly to AROUND(n). The only major difference is that the NEAR operator is used only in the Microsoft ecosystem, particularly Bing and Sharepoint. It returns results where two mentioned terms are mentioned close to each other. It is a flexible way to ensure the terms are contextually related but without specifying the exact number of words apart.
For example, when you search for SEO NEAR Marketer, it will return results where SEO and Marketer are mentioned in proximity, ensuring they are likely being discussed in relation to each other.
intitle:
This operator restricts search results to pages where the specified term appears in the title. It is used only in the Google ecosystem. This is helpful for finding articles, job posts, or content that is specifically about a particular subject. For example, Searching for “intitle:”HR manager” will return pages where HR manager appears in the title.
How to Use Boolean Search in Recruiting?
Here is a detailed breakdown of how to use boolean search in recruitment on different platforms:
Maximizing Recruiter Success with Google Searches
While Google may be a search engine, it is also the go-to place for many recruiters. After all, it has mountains of information about your candidates. However, this also means it is very difficult to sift through the vast database for relevant information.
But with the right Boolean operators, you can make it easy.
For instance, by using the “site:” operator, you can put all your focus on a specific website like Monster. All you need to do is hit the command site:monster.com (Java OR Python) AND developer. This will only return results from Monster containing candidates skilled in Java or Python development.

You can also take advantage of file type searches in Google. This is particularly useful if you are not sure about the platform from where you are sourcing the candidate. For example, you can alter the above example to filetype:pdf (Java OR Python) AND developer resume.
This will return search results where a candidate proficient in Java or Python has uploaded a resume in PDF format, no matter which website.

LinkedIn’s Search Features with Boolean Logic
Unlike Google, LinkedIn is a dedicated recruitment platform. This means it is more user-friendly when it comes to searching for candidates, thanks to several built-in functionalities to narrow the search.
For instance, you could filter profiles by geography, job environment, job duration, level of work experience, and so on.
But that’s not it. You can further fine-tune the search by using dedicated Boolean search strings for recruiters.
LinkedIn’s built-in search function supports all three basic Boolean operators such as AND, OR, and NOT, and advanced Boolean search techniques for recruiters like parentheses and quotation marks.
The wild card operator asterisk does not work, though. Boolean search can be performed on all of their popular platforms, including LinkedIn Basic, LinkedIn Recruiter, and LinkedIn Sales Navigator.
For example, executing the query “MANAGER AND (“ACCOUNTS” OR “FINANCE”) NOT Engineering” on a LinkedIn search will return all the candidates who have been Accounts Managers or Finance Managers. However, if they are engineering graduates, they will not appear.

Other Platforms
Boolean search isn’t limited to just Google and LinkedIn. It can also be applied across a variety of job boards and social media platforms. Ultimately, the goal of Boolean search is to enhance your recruitment efforts, no matter where you are scouring for candidates.
Here are a few more recruitment platforms that support Boolean search:
- Indeed: You can use Boolean searches on Indeed just like you would do on LinkedIn. Enter the string in the Indeed Smart Sourcing module and filter through a vast pool of resumes and job postings. Supported Boolean operators include AND, OR, NOT, Parentheses, and Quotation marks.
- ZipRecruiter: Another popular recruitment platform, ZipRecruiter, allows you to use Boolean search in their advanced RDB search module. Four main operators, AND, OR, parentheses, and quotation marks, are supported in this platform.
- Monster: Monster Jobs, another global player in the recruitment industry, also enables recruiters to use Boolean operators to narrow down search results. Supported operators include AND, OR, NOT, Parentheses, Quotation marks, Wildcare (*), and Proximity (~).
Boolean String Example
Let us now go through three examples of Boolean strings for three specific job titles: Product Manager, UX/UI Designer, and Cybersecurity Specialist. This will give you a better understanding of how the string will change when you are hiring for different positions.
Product Manager Boolean String Example
When searching for a Product Manager, most recruiters would want to include candidates with experience in either of the following:
- Product development
- Project management
- Agile methodology
- Proficiency in a tool like JIRA or Confluence
A Boolean string for this role on a recruitment platform or search engine would look like this:
(“Product Manager” OR “Product Owner”) AND (“Agile” OR “Scrum”) AND (“Product Development” OR “Product Strategy”) AND (“JIRA” OR “Confluence”)
UX/UI Designer Boolean String Example
For a UX/UI Designer role, most recruiters would want to include candidates with experience in either of:
- Designing user interfaces
- Designing user experience
- Proficiency in design tools like Figma or Adobe XD
A Boolean string for this role on a recruitment platform or search engine would look like this:
(“UX Designer” OR “UI Designer” OR “User Experience Designer”) AND (“Figma” OR “Sketch” OR “Adobe XD”) AND (“User Interface” OR “User Experience”)
Cybersecurity Specialist Boolean String Example
For a Cybersecurity Specialist, key skills might include:
- Network security
- Threat detection
- Specific certifications like CISSP or CEH
A Boolean string for this role on a recruitment platform or search engine would look like this:
(“Cybersecurity Specialist” OR “Information Security Analyst”) AND (“Network Security” OR “Threat Detection”) AND (CISSP OR CEH OR “Certified Ethical Hacker”)
Integrating Boolean Search into Recruitment Tools
While using Boolean search on recruitment platforms is indeed useful, it becomes even more helpful when it is integrated into recruitment tools like ATS and CRM platforms.
For instance, using Boolean search in an ATS enables you to filter profiles more precisely and quickly by combining different variables like skills, locations, experience levels, etc.
Similarly, Boolean search, when utilized in CRM tools, allows you to filter and segment candidates based on specific skills or experience.
This helps in re-engaging relevant candidates and building targeted talent pipelines for future opportunities.
Now, let us answer the million-dollar question of how to use Boolean search in an ATS or CRM successfully.
So, first and foremost, familiarize yourself with the platform’s Boolean search capabilities. Because every individual CRM and ATS may have search functionalities that use Boolean search in different ways. Here are some ways to use Boolean search effectively in these tools:
- Custom Tags: Many CRMs and ATS systems allow the creation of custom fields and tags for candidates. You can utilize these to organize candidates based on relevant criteria. When searching, combine Boolean operators with these tags to further narrow down your candidate pool.
- Filter by Status or Activity: You can refine search results by filtering candidates based on their status, such as “active,” “placed,” or “inactive.” This ensures you focus on candidates who are most likely open to new opportunities.
- Save Your Searches: Many CRMs and ATS platforms offer the option to save search queries. By saving your most effective recruiting Boolean search strings, you can easily reuse them when new roles become available.
- Advanced segmentation: Build targeted Boolean queries to filter candidates by skillsets, experience, or location. This will help ensure personalized outreach and engagement via the CRM platform.
- Combine historical data: Use Boolean search to merge past candidate information with current search needs. This will allow you to re-engage candidates who match new opportunities.
Best Practices for Using Boolean Search in Recruitment
Now that you’ve seen how you can use Boolean search in recruiting, here are some best practices you can follow:
💡 Start by outlining the ideal candidate’s skills, experience, education, and qualifications to create precise Boolean queries and save time.
💡 Master both basic operators (AND, OR, NOT) and advanced ones to build refined search strings.
💡 Review and refresh your Boolean queries to align with evolving role requirements and industry trends.
💡 Keep a log of effective search strings that yield strong candidates to save time and maintain consistency.
💡 Try various keyword combinations to adjust your search results; use more OR operators to broaden searches or add AND operators to narrow them down.
💡 Use NOT to filter out candidates who don’t meet your search criteria, focusing only on experienced professionals.
💡 Apply Boolean search techniques for recruiters across different platforms like LinkedIn, job boards, and your ATS to maximize candidate reach.
💡 Keep up with updates to recruitment platforms’ Boolean search functionalities to ensure your queries remain effective.
💡 Regularly assess and refine your Boolean search strategies based on results and changing hiring needs for better candidate outcomes.
Overcoming Common Challenges in Boolean Search
Here are some common challenges you might encounter while performing Boolean search in the recruitment space:

1. Syntax Errors
Syntax errors are common and can lead to incorrect or no results. Always double-check your query for typos, such as misplaced operators or missing parentheses and quotation marks.
2. Broad or Narrow Results
It’s tricky to strike the right balance between broad and narrow results. A vague query yields too many irrelevant profiles, while an overly restrictive one may exclude qualified candidates. To optimize your search, refine your keywords and operators or use built-in filters.
3. Keyword Variations
Candidates express skills in various ways—synonyms, abbreviations, or regional spellings can all impact your search results. To enhance accuracy, research and include all potential variations of your target keywords.
4. Ever-Evolving Data
Candidate profiles frequently change, which can lead to outdated or irrelevant results. Regularly update your search queries to reflect shifts in the online talent market and maintain relevance.
How can Peoplebox help Streamline Candidate Screening?
Boolean search is indeed a game-changer when it comes to streamlining and quickening the whole process of candidate sourcing. But it is still a manual search where you need to enter specific commands every time you need to find a candidate for a specific role.
Even after that, you will still be left out with multiple resumes that you need to manually peruse and arrive at a smaller list of ideal candidates. What if there was a way to automate the whole process?
Yes, there is one, and it is achieved through the AI resume screening function of Peoplebox.
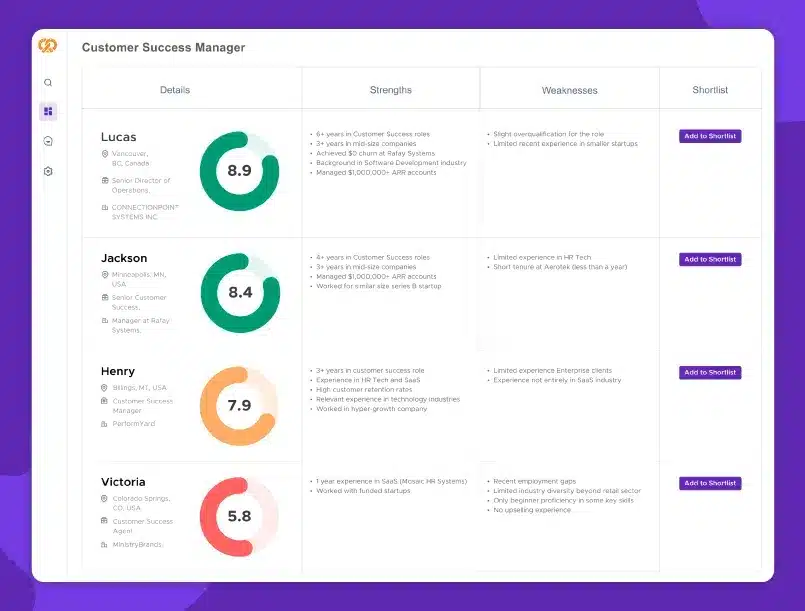
With Peoplebox, you can make smarter and faster hiring decisions thanks to AI-driven insights. This can reduce 90% of applicant review time by quickly narrowing down best candidates. You will get more time to focus on interviews and building meaningful connections.
Apart from this, this feature of Peoplebox can also help identify the right cultural fit and uncover insights beyond job boards and search engines to understand a candidate’s entire journey. Peoplebox even generates scores and shortlists candidates based on key attributes. Want to know more about the capabilities of Peoplebox?
Book a Demo Now!






