If you’re an HR manager or business leader, chances are you’ve heard of Management By Objectives (MBO) – the strategic management approach that’s been around for decades. But what exactly is it, and why should you care?
MBO was pioneered by the legendary management guru Peter Drucker back in the 1950s, and it’s since become a widely adopted management style or framework for aligning individual and team goals with the company goals.
However, is it the best way to drive organizational performance and ensure everyone is on the same page? Let’s find out!

What is Management By Objectives?

MBO is a strategic management approach that emphasizes the collaborative setting of goals between managers and their subordinates. Its primary aim is to ensure that employees’ activities and outputs are aligned with the goals of the organization, thereby improving productivity, efficiency, and accountability.
The key principles that underpin the MBO framework include:
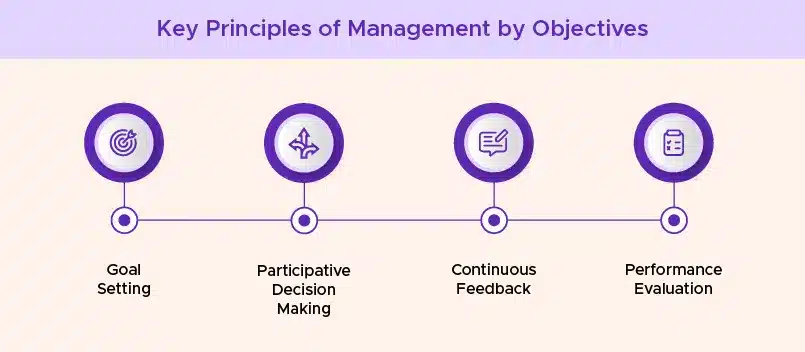
👉 Goal Setting: Establishing clear, measurable, and achievable objectives at the organizational, departmental, and individual goals level. This helps provide a clear direction and focus for the entire organization.
👉 Participative Decision-Making: Involving employees in the goal-setting process to help set their own objectives to foster a sense of ownership and commitment. This collaborative MBO approach helps ensure that objectives are realistic and aligned with the team’s capabilities.
👉 Continuous Feedback: Implementing mechanisms for regular feedback, progress tracking, and adjustments to the objectives as needed. This allows for course corrections and ensures that the organization remains agile and responsive to changing conditions.
👉 Performance Evaluation: Assessing employee performance based on the achievement of pre-defined objectives rather than subjective measures or output-based metrics. This provides a more objective and transparent way to evaluate and reward actual performance.
Types of Objectives in MBO
In the Management by Objectives framework, setting the right types of objectives is crucial for aligning individual and organizational goals. These objectives can be categorized into three main types: strategic, tactical, and operational.
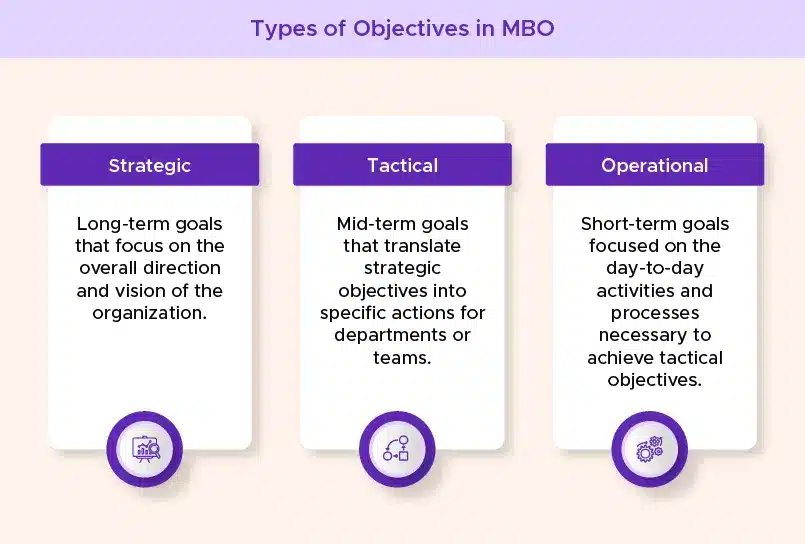
1️⃣ Strategic Objectives
Strategic objectives are long-term, high-level goals that are directly aligned with the organization’s overarching vision and mission. This strategic approach typically has a 3-5-year time frame and focuses on the big-picture priorities that will propel the organization forward. Some examples of strategic objectives include:
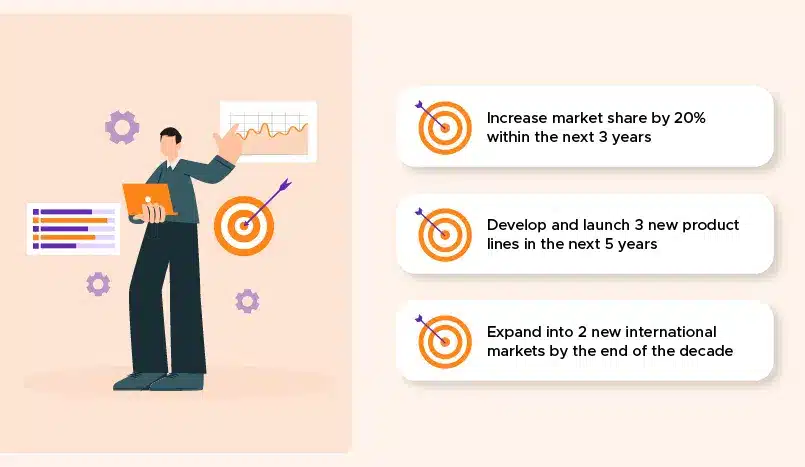
Strategic objectives are crucial because they provide a clear direction and focus for the entire organization. They help ensure that everyone is working towards the same long-term goals and priorities.
2️⃣ Tactical Objectives
Tactical objectives are the mid-term goals that bridge the gap between the organization’s strategic vision and its day-to-day operational activities. These objectives typically have a 1-2 year time frame and are designed to translate the strategic plan into actionable steps. Examples of tactical objectives include:
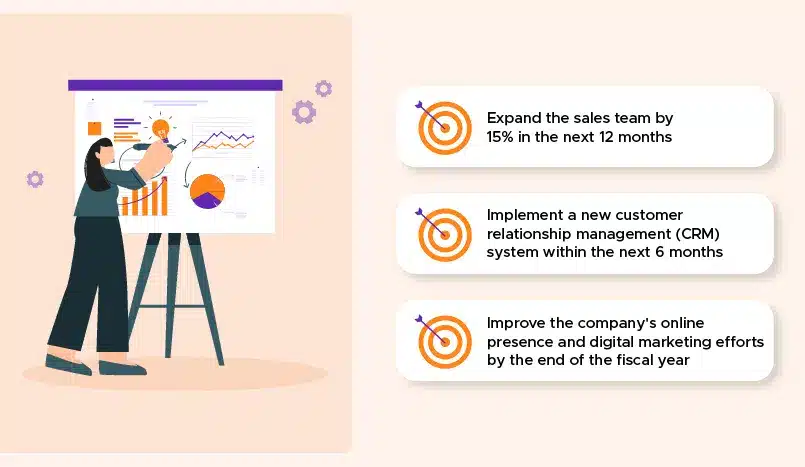
Tactical objectives are essential for ensuring that the organization’s strategic priorities are being actively pursued and measured. They help keep the team focused on the key milestones that will ultimately contribute to the achievement of the overarching strategic goals.
3️⃣ Operational Objectives
Operational objectives are short-term, specific goals that focus on the day-to-day activities and processes within the organization. These specific objectives typically have a quarterly or annual time frame and are designed to drive continuous improvement and optimization.
Examples of operational objectives include:
Operational objectives are crucial because they provide a clear and measurable way to track the organization’s progress on a more granular level. By setting and achieving these short-term goals, employees can directly contribute to the overall success of the organization.
The MBO Process
Now that we’ve covered the key types of objectives within the management by objectives framework let’s dive into the step-by-step process of implementing the MBO management system in your organization.
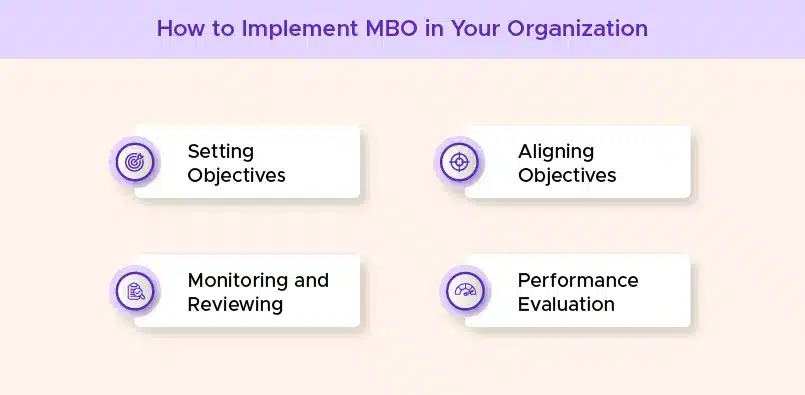
1. Setting Objectives
The foundation of any effective MBO program is the clear and collaborative setting of objectives at different levels of the organization.
Start by engaging your team members in discussions about their individual and departmental goals. Encourage them to share their ideas and insights, as this will help ensure that the objectives are realistic and aligned with their skills and capabilities.
Next, establish a clear hierarchy of objectives, aligning your strategic, tactical, and operational goals into a cohesive and interconnected system. This will help ensure that everyone is working towards the same overarching priorities.
2. Aligning Objectives
One key benefit of MBO is its ability to align individual objectives and team objectives with the organization’s overall goals. To achieve this alignment, start by clearly communicating your organization’s strategic planning and vision and ensuring that everyone understands the big-picture goals and priorities.
Provide clear guidelines and templates for setting and aligning objectives across the organization. This will help maintain consistency and clarity throughout the process.
💡 Encourage cross-functional collaboration by fostering a culture of teamwork and cooperation. Encourage employees to work together towards shared objectives, breaking down silos and promoting a more holistic approach to goal-setting.
3. Monitoring and Reviewing
Effective MBO requires ongoing monitoring and reviewing of progress towards set objectives. Schedule regular check-ins between managers and individual employees to discuss progress, challenges, and any necessary adjustments to objectives based on the overall performance.
Leverage data and analytics to track progress and measure the impact of your MBO system. This will help you make data-driven decisions and course corrections as needed.
4. Performance Evaluation
Finally, MBO provides a clear and objective framework for assessing employee performance based on the achievement of set objectives. Ensure that your performance evaluation system is directly tied to the accomplishment of individual and team goals, reinforcing the importance of the MBO process.
Use performance review as an opportunity to provide employees with constructive feedback and guidance for improvement. This will help them grow and develop in their roles.
💡 Don’t forget to recognize and reward those who have successfully achieved their objectives. Celebrating and incentivizing success will help reinforce the value of the MBO process and is key to employee motivation.
MBO Examples for Various Departments in Your Organization
Let’s explore some examples of how MBO can be implemented in three key areas and across job roles: Marketing, Sales, and Software Product Development.
⚙️ Marketing Team
Objective: Generate 20% of total sales from a new social media marketing campaign within the next quarter.
Marketing Team Breakdown:
👉 Content Creators: Develop engaging social media content (images, videos) aligned with the campaign theme, resulting in a 30% increase in follower engagement.
👉 Social Media Managers: Implement a targeted social media ad campaign to reach a specific audience segment, aiming for a 15% click-through rate on ad posts.
👉 Website Conversion Team: Optimize website landing pages for conversions from social media traffic, targeting a 10% conversion rate for leads generated through the campaign.
💰 Sales Team
Objective: Increase annual recurring revenue (ARR) by 15% for the next fiscal year.
Sales Team Breakdown:
👉 Account Executives: Secure and close deals with new clients, aiming for a 10% increase in their individual sales quota.
👉 Customer Success Managers: Upsell and cross-sell existing customers to existing service tiers or additional products, contributing 5% to the overall ARR growth target.
👉 Sales Development Representatives: Qualify a higher volume of leads through improved lead nurturing processes, aiming for a 20% increase in qualified leads passed to Account Executives.
💻 Software Development Team
Objective: Reduce the number of software bugs reported by customers by 25% within the next six months.
Software Development Team Breakdown:
👉 Quality Assurance (QA) Testers: Increase test coverage by 15% through the implementation of new automated testing frameworks.
👉 Software Developers: Improve code quality by adhering to stricter coding standards and conducting thorough code reviews before feature releases.
👉 DevOps Engineers: Streamline the deployment process by implementing continuous integration and continuous delivery (CI/CD) practices to minimize the introduction of bugs during updates.
Challenges and Limitations of Management By Objectives
While MBO has been used for decades as a goal management technique, it is not without its challenges and limitations. Let’s take a closer look at some of the key issues that organizations may face when implementing MBO.

🎯 Overemphasis on Goals
One key criticism of MBO is the risk of focusing too much on setting and achieving objectives at the expense of other important aspects of management. This can lead to a myopic, numbers-driven approach that neglects factors like organizational culture, employee engagement, and ethical considerations.
🗓️ Short-term Focus
The emphasis on measurable, time-bound objectives in MBO can sometimes lead to a short-term mindset, potentially neglecting long-term business strategy and innovation. Managers may be tempted to prioritize quick wins over more ambitious, transformative goals.
🚫 Resistance to Change
Implementing MBO can face resistance from employees and managers who are accustomed to traditional management approaches or are skeptical of the process. Concerns about increased accountability, transparency, and the potential for conflict can hinder the adoption of MBO and the work environment as a whole.
📊 Measuring Performance
Defining meaningful, measurable, and realistic objectives can be a significant challenge, especially in complex or rapidly changing environments. Quantifying certain aspects of performance, such as employee engagement or customer satisfaction, can be particularly difficult.
As organizations struggle with these challenges, they may find that a different goal-setting framework could be more effective than the management by objectives process. One such alternative is Objectives and Key Results (OKRs), which offers a more collaborative, transparent, and adaptable approach.

Management By Objectives vs OKR
While MBO and OKRs share some similarities, there are notable differences that make OKRs a more effective approach for many businesses. Here’s how they differ:
| Attribute | Management By Objectives | Objectives and Key Results (OKRs) |
| Flexibility | More rigid and structured | More agile and adaptable to change |
| Measurement | Relies on subjective performance evaluations | Emphasizes measurable key results |
| Transparency | Can lead to siloed goal-setting | Promotes greater transparency and visibility of goals |
| Collaboration | Involves employee input, but can feel more top-down | Encourages active employee involvement in goal-setting |
| Alignment | Aims to align individual and team goals with organizational objectives | Tends to be more effective in achieving alignment through a cascading framework |
Why Choose Peoplebox for OKRs?
Choosing the right OKR management tool to manage your OKRs can make a significant difference in achieving your organizational goals. Peoplebox stands out as a comprehensive solution designed to simplify and streamline the OKR process.
Here are just a few reasons why Peoplebox stands out:
✅ User-Friendly Interface: Easy to navigate, allowing teams to quickly set, track, and update their OKRs on the go.
✅ Real-Time Tracking: Provides instant insights into progress, helping teams stay on track and make data-driven decisions.
✅ Integration Capabilities: Seamlessly integrates with other workforce tools and platforms, ensuring a smooth workflow.
✅ Customizable Dashboards: Tailor your dashboards to focus on the metrics that matter most to your organization.
✅ Collaborative Tools: Facilitate communication and collaboration among team members through Slack and Teams, fostering a sense of unity and purpose.
Help your teams to achieve their best with Peoplebox. Get in touch with us today!







