Today, organizations are constantly seeking ways to motivate their employees and drive superior performance. One strategy that has gained significant traction in recent years is the pay for performance model.
However, crafting an effective pay-for-performance plan requires careful consideration of various factors, from performance metrics to communication strategies. In this blog post, we will explore essential elements and best practices for creating a robust pay for performance plan.
Whether you’re looking to enhance your existing compensation structure or develop a new plan, these insights will help you motivate your workforce and drive organizational success.

What is Pay for Performance Compensation?
Pay for performance is a compensation strategy where financial rewards, such as salary increases or bonuses, are directly linked to an employee’s performance and contributions to the organization. This model aims to motivate employees, align individual objectives with company goals, and retain top talent by recognizing and rewarding excellence.

How Does Pay for Performance Work?
Pay for performance involves setting specific, measurable performance metrics that employees are expected to achieve, such as sales targets or customer satisfaction scores. Employees receive financial rewards, such as bonuses or salary increases, based on their success in meeting or exceeding these goals.
This approach aims to motivate employees by aligning their individual contributions with the overall objectives of the organization, fostering a culture of accountability and high performance.
What are the Different Types of Pay for Performance Models?
There are several pay-for-performance models that organizations can adopt to incentivize employee performance and align compensation with results. Here are some of the most common options:
1. Merit-based Pay
Merit pay involves increasing an employee’s base salary based on their performance. Employees who meet or exceed performance goals receive a salary raise during annual performance appraisals.
This model is widely used as it allows organizations to differentiate between high and low performers, but it may not provide immediate rewards for outstanding performance since adjustments are typically made once a year.
2. Variable Pay
Variable pay includes bonuses and incentive pays that vary based on performance metrics. This model can take many forms, such as:
Performance Bonuses: Employees receive additional compensation for achieving specific targets or milestones.
Sales Commissions: Employees earn a percentage of sales they generate, often with tiered commission rates that increase with higher sales volumes.
3. Profit Sharing
In a profit-sharing model, employees receive a portion of the company’s profits, typically distributed annually. This approach aligns employee interests with the overall success of the organization, encouraging teamwork and collaboration to achieve collective goals.
4. Stock Options and Equity Compensation
Employees are granted stock options or equity in the company, allowing them to benefit from the company’s growth and success.
This model fosters a sense of ownership and long-term commitment among employees, as their financial success is tied to the performance of the organization.
5. Team-Based Incentives
Team-based incentives reward groups of employees for achieving collective goals. This model encourages collaboration and teamwork, as employees work together to meet performance targets. It can help mitigate the potential downsides of individual competition that can arise in other pay-for-performance structures.
How is Performance Linked to Compensation?
Performance management is the backbone of fair and transparent compensation. It sets clear expectations, tracks progress, and provides feedback to ensure employees know how their efforts impact their pay.
By identifying top performers and recognizing their contributions, organizations can align pay structures to reward excellence. Regular evaluations and constructive criticism create a culture where employees see a direct link between their work and compensation, keeping them motivated and focused on growth.
Using OKRs and performance management software like Peoplebox.ai makes this process even smoother, offering real-time feedback and ensuring performance goals are always connected to compensation strategies.
What are the Benefits of Pay for Performance?
A well-implemented pay for performance system can drive success and growth for any organization. Here’s how:
Enhanced Employee Motivation
Pay for performance directly ties financial rewards to individual and team achievements. This creates a powerful incentive for employees to excel in their roles, fostering a motivated and engaged workforce.
Increased Productivity
The correlation between the employee’s performance and their compensation plan encourages them to strive for higher levels of productivity. Knowing that their efforts directly impact their earnings motivates individuals to work more efficiently and contribute to organizational goals.
Attracting and Retaining Top Talent
A well-structured pay-for-performance system can attract high-calibre, quality talent by offering competitive compensation aligned with performance. Additionally, it helps retain top performers who seek recognition and reward for their exceptional contributions.
Alignment with Organizational Goals
Pay for performance ensures that individual and team efforts are closely aligned with the strategic objectives of the organization. Employees become more aware of the company’s mission, resulting in a more cohesive and goal-oriented workforce.
Now that we’ve covered the basics, let’s examine how you can implement the pay-for-performance system in your organization.

A Step-by-Step Process of Implementing a Pay for Performance Plan
Creating a strong pay-for-performance system requires strategic planning to ensure it aligns with company goals, fosters motivation, and enhances workplace culture. Follow these key steps to build and implement an effective plan:
Step 1: Understanding Organizational Goals
1.1: Strategic Focus
Start by identifying your company’s primary objectives. Your pay-for-performance plan should directly support these goals, ensuring employee contributions drive overall business success.
1.2: Define Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
Establish measurable KPIs that track progress toward your company’s goals. These will serve as benchmarks for evaluating employee and team performance.
Here’s an example of how KPIs can be identified and defined for different organizational goals:
| Organizational Goal | Key Performance Indicator (KPI) |
| Increase Sales Revenue | – Monthly Sales Revenue Growth Percentage |
| – Number of New Clients Acquired | |
| – Average Transaction Value | |
| Improve Customer Satisfaction | – Customer Net Promoter Score (NPS) |
| – Percentage of Positive Customer Feedback | |
| – Resolution Time for Customer Inquiries | |
| Enhance Employee Productivity | – Individual and Team Project Completion Time |
| – Percentage Increase in Output | |
| – Employee Utilization Rate | |
| Strengthen Market Presence | – Market Share Growth Percentage |
| – Brand Recognition Index | |
| – Number of Positive Media Mentions | |
| Ensure Regulatory Compliance | – Number of Compliance Violations |
| – Timely Completion of Compliance Audits | |
| – Employee Training Completion Rates |
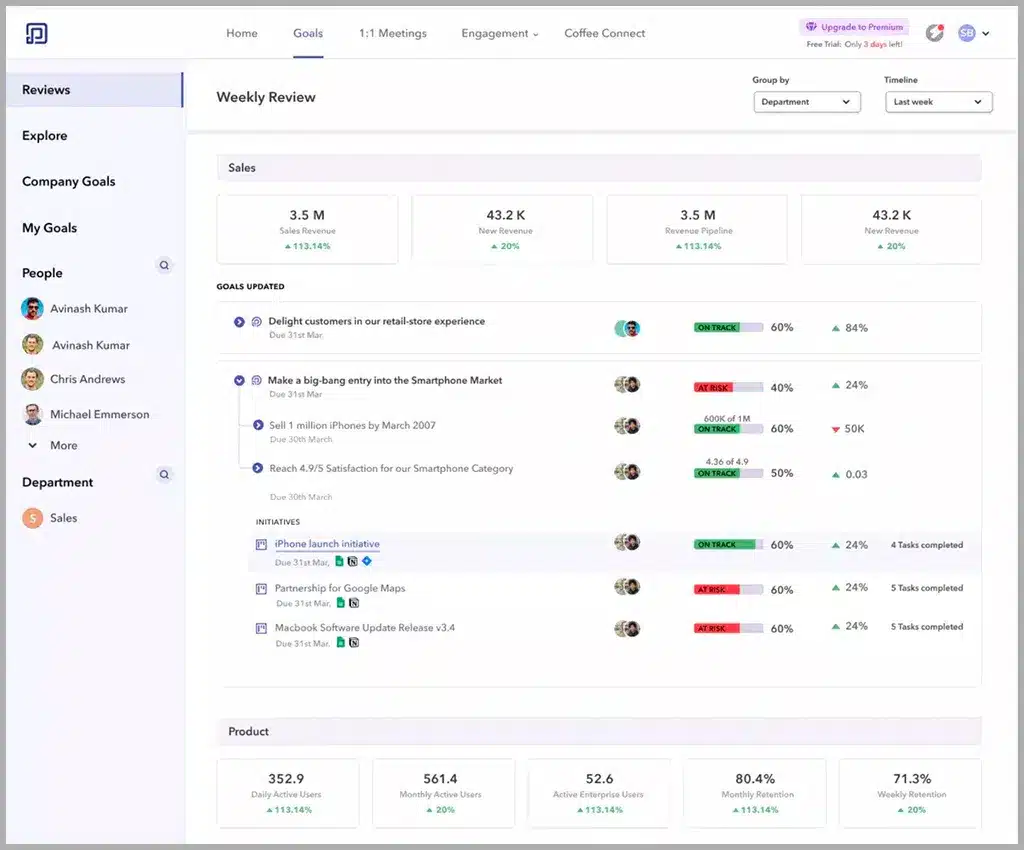
With Peoplebox.ai, you can effortlessly craft personalized and professional KPI dashboards in minutes.
Step 2: Crafting Individual Performance Metrics
To ensure a successful pay-for-performance plan, it’s essential to establish precise, measurable objectives for each role. These performance metrics should align with company goals and encourage employees to contribute effectively.
2.1: Set Clear and Measurable Objectives
Establish clear and measurable performance objectives for each role within the organization. These objectives should be directly connected to the identified KPIs and contribute to the broader organizational strategy.
Objectives and Key Results provide a structured approach to setting performance goals by emphasizing clear objectives, measurable outcomes, and continuous improvement. This method fosters a culture of accountability, alignment, and collaboration, ensuring employees stay focused on driving success.
If this is the first time you have heard of OKRs, our OKR cheat sheet can help you understand them in depth.
2.2: Define Quantifiable Targets
Setting specific and measurable targets gives employees a clear direction. Examples include:
✅ Sales Representatives → Achieve a 15% increase in monthly sales.
✅ Project Managers → Deliver 90% of projects on time.
✅ Customer Support → Maintain an 85%+ customer satisfaction score.
Step 3: Determining Compensation Structure
Creating an effective pay-for-performance model requires a well-structured compensation plan that rewards employees for their contributions while maintaining fairness and transparency.
3.1: Incorporate Variable Pay Components
A strong compensation plan should include performance-based pay elements, such as:
✅Performance Bonuses – Reward employees for exceeding targets
✅Profit-Sharing – Align employee success with company growth
✅Commission Structures – Provide direct incentives for revenue-generating roles
3.2: Ensure Fair and Transparent Criteria
Employees should have a clear understanding of how performance impacts their earnings. To build trust and engagement, organizations must:
✅ Clearly define eligibility criteria for bonuses and incentives
✅ Maintain objective and consistent evaluation processes
✅ Communicate performance expectations openly
Step 4: Communication and Employee Engagement
For a pay-for-performance model to succeed, employees must understand, trust, and actively engage with the process. Transparent communication and employee involvement are key to building a motivated and accountable workforce.
4.1: Transparent Communication
Employees should have a clear picture of how their performance impacts both organizational success and their compensation. To achieve this:
- Explain the link between performance and rewards
- Outline the criteria for bonuses and incentives
- Ensure managers provide regular feedback
4.2: Achieve Employee Involvement
Encourage employees to take ownership of their performance by involving them in goal-setting. When employees help define their own performance objectives, they feel:
✅ More invested in achieving success
✅ Empowered to take initiative
✅ Accountable for their progress
Did you know, Peoplebox.ai lets you do a LOT right within your favourite collaboration tools?
Step 5: Continuous Monitoring and Evaluation
A pay-for-performance plan is only effective if it’s regularly assessed and refined. Ongoing monitoring ensures employees stay aligned with goals, receive meaningful feedback, and have opportunities to continuously improve.
5.1: Regular Performance Reviews
Implement regular performance reviews to assess progress toward the set goals and provide constructive feedback.
Frequent check-ins and performance reviews help:
- Track progress toward set goals
- Provide constructive feedback for improvement
- Recognize and celebrate achievements
This ongoing evaluation ensures that employees are aware of their quality of work, performance levels and areas for improvement.
5.2: Flexibility for Adjustments
A rigid pay-for-performance plan can become outdated as business goals evolve. To maintain effectiveness:
✅ Adapt performance metrics based on business shifts
✅ Refine compensation criteria as needed
✅ Ensure fairness in changing circumstances
Step 6: Employee Development and Recognition
A pay-for-performance plan isn’t just about financial rewards—it should also support growth and appreciation. Investing in employees’ development and recognizing their contributions strengthens motivation and long-term commitment.
6.1: Professional Development Opportunities
Tie performance to learning and career growth by offering:
✅ Skill-building workshops & training
✅ Mentorship & coaching programs
✅ Opportunities for leadership development
6.2: Recognition Programs
Beyond monetary rewards, publicly celebrating achievements fuels motivation and strengthens company culture. Recognize top performers through:
✅Employee of the Month awards
✅Shoutouts in team meetings or internal platforms
✅Personalized appreciation from leadership
Don’t forget to check out our quick guide to employee recognition in 2024.
Step 7: Regular Plan Evaluation and Iteration
A pay-for-performance plan should evolve alongside your organization. Regularly assessing its effectiveness ensures it stays fair, motivating, and aligned with business goals.
7.1: Performance Metrics Review
✅ Analyze if the chosen metrics are driving desired outcomes.
✅ Adjust or refine metrics that don’t align with company objectives.
✅ Ensure accuracy in measurement to maintain fairness and credibility.
7.2: Employee Feedback Integration
✅Gather employee feedback on the plan’s fairness and impact.
✅Use their insights to fine-tune and improve the structure.
✅Foster a culture of continuous improvement and transparency.
Here’s a quick look at how easy it is to create surveys on Peoplebox.ai.
While the pay for performance model comes with its own perks, we must note that there are some challenges you might encounter while implementing the model
While the pay for performance model comes with its own perks, we must note that there are some challenges you might encounter while implementing the model
Cons of Pay for Performance System
Subjectivity and Bias
- Performance evaluations can be influenced by unconscious bias or favoritism.
- Subjective reviews may lead to unfair rewards.
Solution: Use performance management systems tools like Peoplebox.ai to ensure fair, objective, and bias-free evaluations.
Short-Term Focus
- Employees may prioritize quick wins over long-term strategic goals.
- This focus on immediate rewards can stifle innovation and growth.
Solution: Ensure individual goals are aligned with overarching business objectives using platforms like Peoplebox.ai for a holistic approach.
Employee Burnout
- The constant pressure to perform for financial rewards can lead to stress and exhaustion.
- This can negatively impact job satisfaction, morale, and overall well-being.
Collaboration Challenges.
- When rewards are tied strictly to individual performance, teamwork may suffer.
- Employees might hesitate to share knowledge or support colleagues.
Unintended Consequences and Unhealthy Competition
- An overly competitive environment can reduce cooperation and increase workplace tension.
- Employees may focus more on personal success rather than team growth.
Before adopting a pay-for-performance model, conduct a thorough assessment of your company culture, industry, and workforce dynamics to ensure it aligns with your long-term success!
Tips for an Effective Pay for Performance Strategy
Bridging the gap between performance and compensation can be tricky. Here are some tried and tested strategies you can use for a seamless pay system..
1. Strategic Alignment Communication
- Ensure employees understand how their performance aligns with the company’s goals.
- Using a strategy execution platform like Peoplebox.ai provides a holistic view of the organization, making it easier to communicate this alignment effectively.
2. Transparent Criteria Communication
- Clearly outline the criteria for performance evaluations and compensation decisions.
- Transparency builds trust and reduces uncertainty.
- Identify key performance review competencies and communicate them openly to all employees.
3. Regular Communication Channels
✅Keep employees informed through consistent updates on:
- Performance expectations
- Progress reports
- Compensation structure changes
✅Regular communication reinforces a shared understanding of performance objectives.
4. Equitable Evaluation Criteria
- Implement fair and objective evaluation standards.
- Ensure all employees are assessed equally, fostering a culture of fairness.
Check out our latest article on “5 ways to improve diversity and inclusion in the workplace“!
5. Merit-Based Compensation
- Tie compensation directly to individual achievements.
- A merit-based pay structure drives motivation and a culture of excellence.
6. Open Performance Discussions
- Encourage open conversations about expectations, goals, and outcomes.
- This allows employees to be actively engaged in their development and understand the rationale behind pay decisions.
7. Accessible Compensation Information
- Ensure employees can easily access and understand their compensation package.
- Clearly explain base pay, bonuses, and any variable pay components to promote fairness and clarity.
How to Measure the Impact of Pay for Performance?
Measuring the impact of pay for performance plans is essential for understanding their effectiveness in driving employee engagement, retention, and overall organizational performance. Here’s a quick look at how to assess these outcomes.
Assessing Employee Engagement
Employee Satisfaction Surveys
- Conduct regular employee surveys to gauge employee satisfaction with the pay for performance system.
- Inquire about perceived fairness, motivation levels, and the system’s influence on their commitment to organizational goals.
Participation in Performance Programs
- Measure the level of employee engagement by analyzing participation rates in performance improvement programs linked to the pay for performance structure.
- Higher participation may indicate a positive impact on engagement.
Feedback Mechanisms
- Establish transparent channels for employees to provide feedback on the pay for performance system.
- Regular feedback sessions can reveal insights into employee perceptions and areas for improvement.
Evaluating Employee Retention
Retention Rates
- Compare employee retention before and after implementing pay-for-performance.
- A decrease in employee turnover may signify that the pay for performance system is contributing to employee satisfaction and loyalty.
Exit Interviews
- Conduct thorough exit interviews to understand both the internal and external factors behind employee departures.
- Analyze whether dissatisfaction with the pay for performance system is a contributing factor.
Promotion and Advancement
- Track employee promotions and advancements.
- A rise in promotions suggests that high performers are being recognized and rewarded effectively, boosting employee retention.
Gauging Organizational Performance
Productivity Metrics
- Analyze changes in productivity metrics following the implementation of the pay for performance system.
- Increased productivity may indicate that employees are motivated to perform at higher levels.
Financial Performance
- Assess the overall financial performance of the organization.
- A positive correlation between the pay for performance system and financial outcomes may signify the effectiveness of the incentive structure.
Employee Contributions to Organizational Goals
- Evaluate how well individual and team contributions align with organizational objectives.
- The pay for performance system’s impact on goal alignment can be indicative of its influence on overall organizational performance.
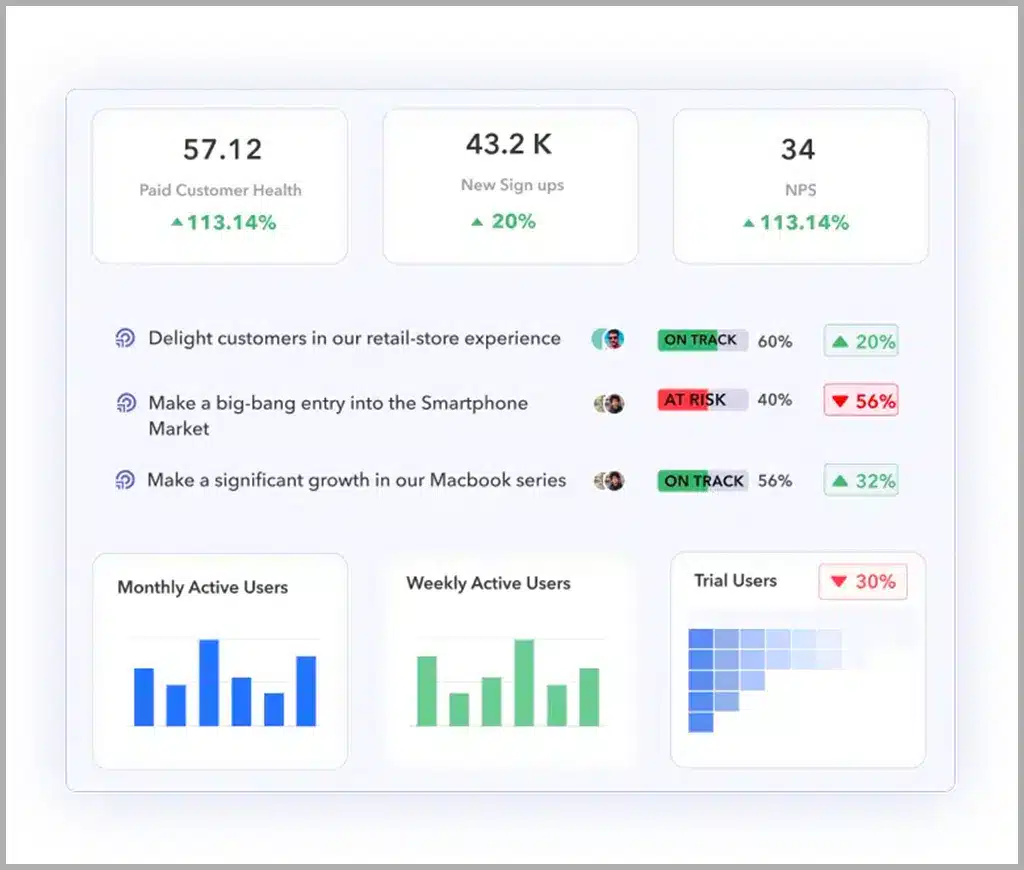
Leveraging Peoplebox.ai for Performance-Driven Compensation
Peoplebox’s.ai performance management features offer a robust platform for creating a seamless and effective pay for performance plan. The platform facilitates goal setting and alignment, enabling organizations to establish OKRs that directly link employee efforts to overarching business goals.
With continuous performance evaluation and data-driven insights, Peoplebox.ai empowers organizations to make informed compensation decisions based on actual performance outcomes, fostering a culture of meritocracy and fairness.
Start your journey towards a high-performing workforce by embracing Peoplebox.ai today. Get in touch with us.







