Performance coaching isn’t just about giving feedback it’s about empowering your employees to reach new heights and drive organizational success. When done right, coaching fuels growth, engagement, and peak performance.
As a manager, implementing an effective performance coaching strategy can significantly impact employee engagement, productivity, and job satisfaction. This comprehensive guide explains everything you need to know about performance coaching to effectively guide your team towards success.
Use Peoplebox.ai for streamlined coaching and progress tracking.

What Do You Mean By Performance Coaching?
Performance coaching is an ongoing process where a manager works with individual employees to identify their strengths, weaknesses, and goals. It’s not about micromanaging or dictating instructions; it’s about creating a supportive environment where employees can learn, develop, and excel.
Performance Coaching Example in Action
Consider Rhea, a marketing manager responsible for guiding a team of content creators. Rather than simply delegating tasks and expecting results, Rhea implements performance coaching strategies to nurture her team’s development.
Regular one-on-one meetings are a staple of Rhea’s coaching approach. In these sessions, she listens attentively to her team members’ insights and concerns, offering constructive feedback and guidance to help them progress toward their goals.
Take Alan, one of Rhea’s team members, aiming to refine his copywriting skills. Rhea doesn’t just assign more tasks. Instead, she collaborates with Alan, devising a tailored development plan. With Rhea’s support, Alan sees tangible improvements, boosting both his work quality and job satisfaction.
Doesn’t that sound great? Well, that’s how significant performance coaching can be in the workplace. Let’s take a quick look at why performance coaching should be implemented at your workplace.
How Can Coaching Improve Performance?
Performance coaching is crucial in the workplace for several key reasons:
1. Drives Individual Growth and Satisfaction
Empowerment and Ownership
Coaching fosters a sense of ownership and control over personal development, motivating employees to take initiative and invest in their own growth.
Meaningful Learning
Targeted skills development based on individual needs ensures learning is relevant and impactful, increasing essential motivation and engagement.
Personalized Support
Tailored coaching addresses specific strengths and weaknesses, creating a safe space for feedback and growth, leading to next-level job satisfaction and well-being.
2. Enhances Retention and Performance
Reduced Turnover
Employees who feel valued and supported through coaching are less likely to leave, reducing costly employee turnover and its associated disruptions.
Improved Performance
Continuous feedback, goal setting, and skill development lead to demonstrably improved performance metrics and a culture of high performance.
Stronger Teamwork
By addressing areas for improvement openly and collaboratively, coaching fosters healthy team dynamics and builds trust, resulting in smoother collaboration and higher output.
3. Cultivates a High-Performing Culture
Open Communication
Regular coaching conversations normalize open communication, facilitating transparency and problem-solving across all levels.
Shared Goals and Values
Collaborative coaching aligns individual goals with organizational objectives, creating a shared sense of purpose and direction.
Continuous Improvement
The focus on learning and development ingrained in coaching becomes part of the organizational DNA, fostering a culture of continuous improvement and innovation.
4. Provides Competitive Advantage
Enhanced Employer Branding
Organizations known for investing in employee growth attract top talent, giving them a competitive edge in the market.
Increased Innovation
A culture of learning and development leads to a more adaptable workforce, able to generate innovative solutions and stay ahead of the curve.
Stronger Customer Relationships
When employees are empowered and engaged, they deliver exceptional customer service, driving loyalty and business growth.
Investing in performance coaching is not just about fixing problems; it’s about unleashing the full potential of your employees and organization. By fostering growth, engagement, and work performance, you create a winning formula for individual and organizational success in today’s competitive landscape.
Performance Coaching Examples at Work
While the benefits of performance coaching are clear, seeing it in action can solidify its value. The examples below showcase how performance coaching, tailored to different situations, can benefit individuals and teams.
1. Helping a New Employee Transition Smoothly
The Challenge
A new employee struggles to adapt to the company culture and expectations. They may feel overwhelmed by the unfamiliar environment, unclear about their role and responsibilities, and unsure of how to navigate the organization effectively.
Coaching Approach
In this type of coaching scenario, the manager plays a crucial role in helping the new employee transition smoothly. The coaching approach involves:
1. Providing regular check-ins
The manager schedules frequent one-on-one meetings to assess the employee’s progress, address any concerns, and offer guidance and support.
2. Mentoring from experienced colleagues
Pairing the new employee with a seasoned colleague who can share insights, offer advice, and provide a supportive network can greatly facilitate the onboarding process.
3. Clear expectations and performance goals
The manager clearly communicates the company’s culture, values, and expectations, and works with the employee to set achievable performance goals that align with organizational objectives.
The Outcome
The new employee quickly gains confidence, adapts seamlessly, and becomes a productive team member faster setting the stage for long-term success.
2. Coaching an Underperforming Employee Back on Track
The Challenge
An employee consistently misses deadlines, delivers poor work, and exhibits low productivity. This underperformance can negatively impact team dynamics, project outcomes, and overall organizational efficiency.
Coaching Approach
When dealing with an underperforming employee, the manager should take a proactive and supportive coaching approach:
1. Conducting a one-on-one meeting
The manager schedules a private meeting to discuss the employee’s performance issues, explore underlying reasons for the underperformance, and gain a better understanding of the employee’s perspective.
With performance management software like Peoplebox.ai, you can set up one-on-ones in minutes. Try it yourself!
2. Setting OKRs (Objectives and Key Results)
The manager collaborates with the employee to set clear, measurable objectives and key results that address the performance gaps and provide a framework for improvement.
3. Providing specific skill development resources
Based on the identified performance gaps, the manager offers targeted training, workshops, or mentoring opportunities to help the employee acquire the necessary skills and knowledge to improve their performance.
Outcome
With structured support, the employee identifies productivity blockers, gains motivation, and delivers stronger results benefiting both them and the organization.
3. Unlocking the Potential of a High-Performing Employee
The Challenge
An employee demonstrates strong potential, consistently exceeds performance expectations, and shows a keen interest in growth and advancement. However, they may lack specific leadership skills or experience required for higher-level roles.
Coaching Approach
To nurture and develop the high-potential employee, the manager should adopt a coaching approach that challenges and supports their growth:
1. Assigning challenging projects
The manager provides opportunities for the employee to take on stretch assignments that push their boundaries, allowing them to develop new skills and gain valuable experience.
2. Providing leadership training
The manager ensures that the employee has access to leadership development programs, workshops, or coaching sessions to build essential leadership competencies such as decision-making, communication, and team management.
3. Facilitating opportunities for mentoring and shadowing senior leaders
The manager connects the employee with senior leaders or executives who can provide guidance, share their experiences, and offer valuable insights into leadership roles and responsibilities.
The Outcome
By implementing this coaching approach, the high-potential employee gains the necessary skills, experience, and exposure to prepare for future advancement opportunities. They feel empowered, motivated, and confident in their ability to take on greater responsibilities and contribute to the organization’s success at a higher level.
4. Resolving Conflict Between Team Members
Challenge
Two team members have a recurring conflict that stems from personality differences, communication breakdowns, or misaligned expectations. This conflict can disrupt team dynamics, hinder collaboration, and negatively impact overall team performance.Two employees frequently clash, leading to communication breakdowns and reduced team efficiency.
Coaching Approach
In this scenario, the manager should take on the role of a conflict resolution coach, facilitating a process that helps the team members resolve their differences:
1. Facilitating a joint coaching session
The manager brings the conflicting parties together in a private setting to discuss the issues openly and honestly, encouraging them to express their concerns and perspectives.
2. Encouraging open communication
The manager fosters an environment of trust and respect, guiding the team members to communicate effectively, actively listen to each other, and seek to understand different viewpoints.
3. Helping identify underlying issues
The manager probes deeper to uncover the root causes of the conflict, such as misunderstandings, unmet expectations, or personal biases, and helps the team members gain clarity on the real issues at hand.
Outcome
By implementing this coaching approach, the conflicting team members improve their communication skills, develop a better understanding of each other’s perspectives, and find mutually agreeable solutions to resolve the conflict. This process helps to restore team dynamics, enhance collaboration, and improve overall team performance.With improved communication and mutual respect, the employees work together more effectively, boosting team collaboration and morale.
5. Empowering an Employee with Career Growth Planning
Challenge
An employee feels stuck in their current role, unsure of their career progression options within the organization.
They may lack clarity on their strengths, interests, and how to align them with available opportunities for growth and advancement.
Coaching Approach
To help the employee navigate their career path, the manager should adopt a coaching approach that focuses on self-discovery and exploration:
1. Conducting career discussions
The manager schedules regular one-on-one meetings to discuss the employee’s career aspirations, interests, and goals, and helps them identify potential paths for growth and development within the organization.
2. Helping identify strengths and interests
The manager guides the employee through self-assessment exercises, such as personality tests or skills inventories, to help them gain a better understanding of their strengths, values, and interests, and how they align with potential career options.
3. Exploring internal opportunities and training programs
The manager provides information about available internal job opportunities, cross-training programs, or leadership development initiatives that align with the employee’s career goals and help them acquire new skills or gain relevant experience.
Outcome
By implementing this coaching approach, the employee feels empowered, supported, and in control of their career development. They gain clarity on their strengths, interests, and career goals, and develop a roadmap for achieving their desired career path within the organization.
This process helps to boost employee engagement, retention, and overall job satisfaction.With a clear roadmap for career growth, the employee feels empowered, engaged, and motivated leading to long-term retention and job satisfaction.
5 Steps to Implement Performance Coaching in Your Organization
Performance coaching is a powerful tool to help employees do their best, but navigating the process can seem daunting. Here’s a step-by-step guide to implementing performance coaching like a pro.
Step 1: Identify Needs
✅Listen actively: During regular conversations and performance reviews, identify individual strengths, weaknesses, and development areas. Encourage open communication and honest feedback.

✅Analyze performance: Look at metrics, project outcomes, and team dynamics to identify areas for improvement at the team level.
✅Align with goals: Connect identified needs to individual and organizational goals. Focus on areas that will have the most impact on performance and career development.
Step 2: Set the Stage for Success
Communicate clearly: Explain the purpose and benefits of performance coaching to your team. Encourage them to see it as an opportunity for growth, not criticism.
Set expectations: Define clear roles and responsibilities for both you and your employees. Establish communication protocols and confidentiality measures.
Choose your model: Select a coaching model that aligns with your goals and team dynamics. We will cover some of the most popular performance coaching models below.
Step 3: Craft a Winning Coaching Journey
✅Goal setting: Collaboratively set OKRs with each employee, aligning them with individual needs and organizational objectives.
If you’re new to OKRs, we cover everything you need to know about it in our free OKR cheat sheet. Check it out!
✅Regular check-ins: Schedule regular one-on-one coaching sessions to provide feedback, discuss progress, and adjust goals as needed.
With Peoplebox.ai, managers can effortlessly schedule and manage one-on-one meetings with their team members.

🌱 Development planning: Based on individual needs, identify relevant training, resources, or opportunities to support skill development.
✅Development planning: Based on individual needs, identify relevant training, resources, or opportunities to support skill development.
Step 4: Coach with care
✅Focus on strengths: Start by acknowledging and appreciating strengths to build trust and rapport.
✅Provide constructive feedback: Be specific, actionable, and focus on behavior change, not personality attacks.
✅Ask open-ended questions: Encourage dialogue and active participation to uncover underlying issues and identify solutions together.

Step 5: Celebrate Wins & Keep Adapting
✅Recognize achievements: Small wins matter! Celebrate good performance and milestones to maintain motivation and reinforce positive behavior.
✅Adapt and adjust: Be flexible and willing to adjust goals, plans, and approaches based on progress and feedback.
Remember: Performance coaching is a journey, not a destination. By following these steps, creating a supportive environment, and continuously learning, you can empower your team members to reach their full potential and drive organizational success?
Bonus tip: Consider incorporating technology tools for scheduling, progress tracking, and feedback exchange to streamline the coaching process.
With performance management platforms like Peoplebox.ai, you don’t have to worry about juggling multiple tools for each task.
What are some Employee Performance Coaching Models?
Performance coaching offers a variety of models to guide your approach, each with its own strengths and ideal applications. Here are some popular models to consider:
1. GROW Model : A Roadmap to Success
Focus: Goal setting and action planning.
Stages:
✅ Goal – What do you want to achieve?
✅ Reality – Where are you now?
✅ Options – What strategies could help you get there?
✅ Will – What specific actions will you take?
Benefits: The GROW model is simple yet powerful, helping employees clarify their goals and map out actionable steps to success.
Example: A sales manager helps a struggling rep boost their closing rate by 10%. Together, they explore current challenges, brainstorm selling techniques, and commit to actionable steps to hit the target.
2. STAR Model : Structure Your Feedback Like a Pro
Focus: Providing effective feedback.
Stages: Situation (Describe the context), Task (What was the goal?), Action (What did you do?), Result (What was the outcome?).
Stages:
✅Situation – What was the context?
✅Task – What was the goal?
✅Action – What did they do?
✅Result – What was the outcome?
Benefits: The STAR model ensures feedback is structured, specific, and actionable, promoting growth instead of confusion.
Example: A marketing manager uses the STAR model to provide feedback to a designer about a presentation. They discuss the target audience, the presentation objectives, the designer’s choices, and the audience’s reaction, offering suggestions for improvement in future presentations.
3. OSCAR Model : Shift Focus to Solutions
Focus: Solution-oriented coaching.
Stages: Outcome (What do you want?), Situation (What’s happening now?), Choices (What options do you have?), Actions (What will you do?), Review (How will you track progress?).
✅Outcome – What’s the end goal?
✅Situation – What’s happening now?
✅Choices – What options are available?
✅Actions – What steps will you take?
✅Review – How will progress be tracked?
Benefits:.Instead of dwelling on problems, the OSCAR model encourages employees to take ownership of solutions.
Example:.A team leader supports an overwhelmed employee by helping them prioritize tasks, brainstorm time-management solutions, and set up a system to track their progress effectively.
4. 70/30/0 Model : The Feedback Sweet Spot
Focus: Balancing feedback and development.
Principles:.
✅70% on strengths and positive reinforcement
✅30% on areas for development
✅0% on blame or negativity
Benefits: Builds trust and confidence, motivates ongoing training and learning.
Example: A manager using the 70/30/0 model commends an employee for their strong analytical skills (70%), then points out an area where they could improve communication (30%), and offers resources for communication training.
5. CLEAR Model : Build Trust and Drive Change
Focus: Building a strong coaching relationship.
Stages: Contract (Establish agreements and expectations), Listen (Actively listen and understand), Explore (Ask the right questions and delve deeper), Action (Develop a plan together), Review (Track progress and adjust).
✅Contract – Set clear expectations for coaching
✅Listen – Actively understand challenges and concerns
✅Explore – Ask deep, thought-provoking questions
✅Action – Co-create an actionable plan
✅Review – Regularly track progress and refine the plan
Benefits: Fosters open communication and trust, creates a collaborative environment.
Example: A performance coach using the CLEAR model starts by defining the boundaries and goals of the coaching relationship, actively listens to the coach’s concerns, helps them explore their challenges, develops an action plan together, and schedules regular check-ins to monitor progress and adapt the plan as needed.
Remember, the best model isn’t a one-size-fits-all solution. Choose the model that best aligns with your specific situation, individual needs, and desired coaching outcomes for the most effective results.
Using Peoplebox.ai for Continuous Performance Management
Peoplebox.ai offers a comprehensive platform designed to streamline and enhance the performance management process, making it a valuable tool for managers and employees alike. Here’s how you can leverage Peoplebox.ai for effective performance reviews:
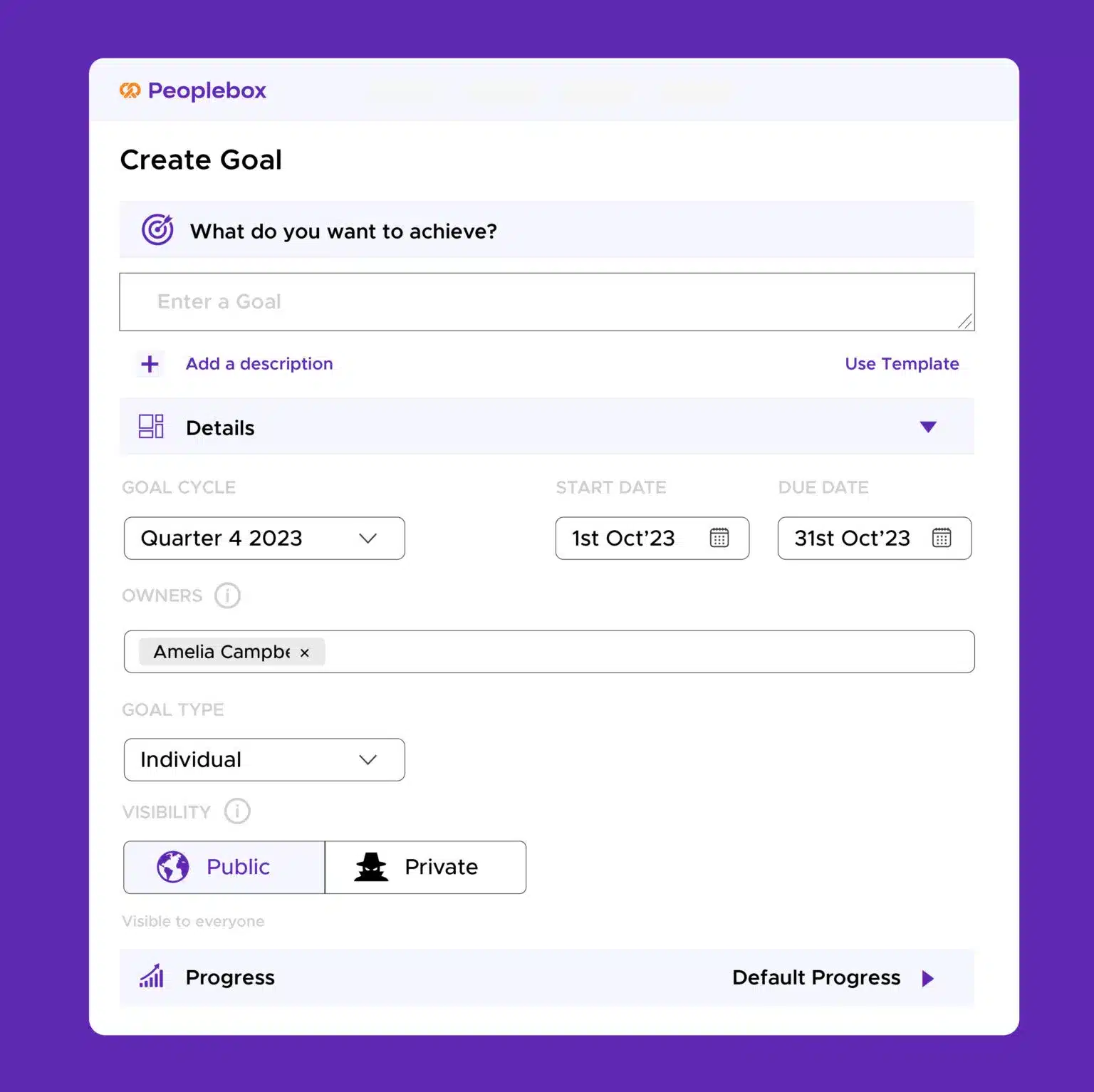
Goal Definition & Expectation Setting
Easily set OKRs for individuals and teams to align with organizational goals, clarifying responsibilities and contributions.
360-Degree Feedback
Collect feedback from peers, managers, and direct reports through 360-Degree Feedback for a comprehensive view of performance, strengths, and improvement areas.
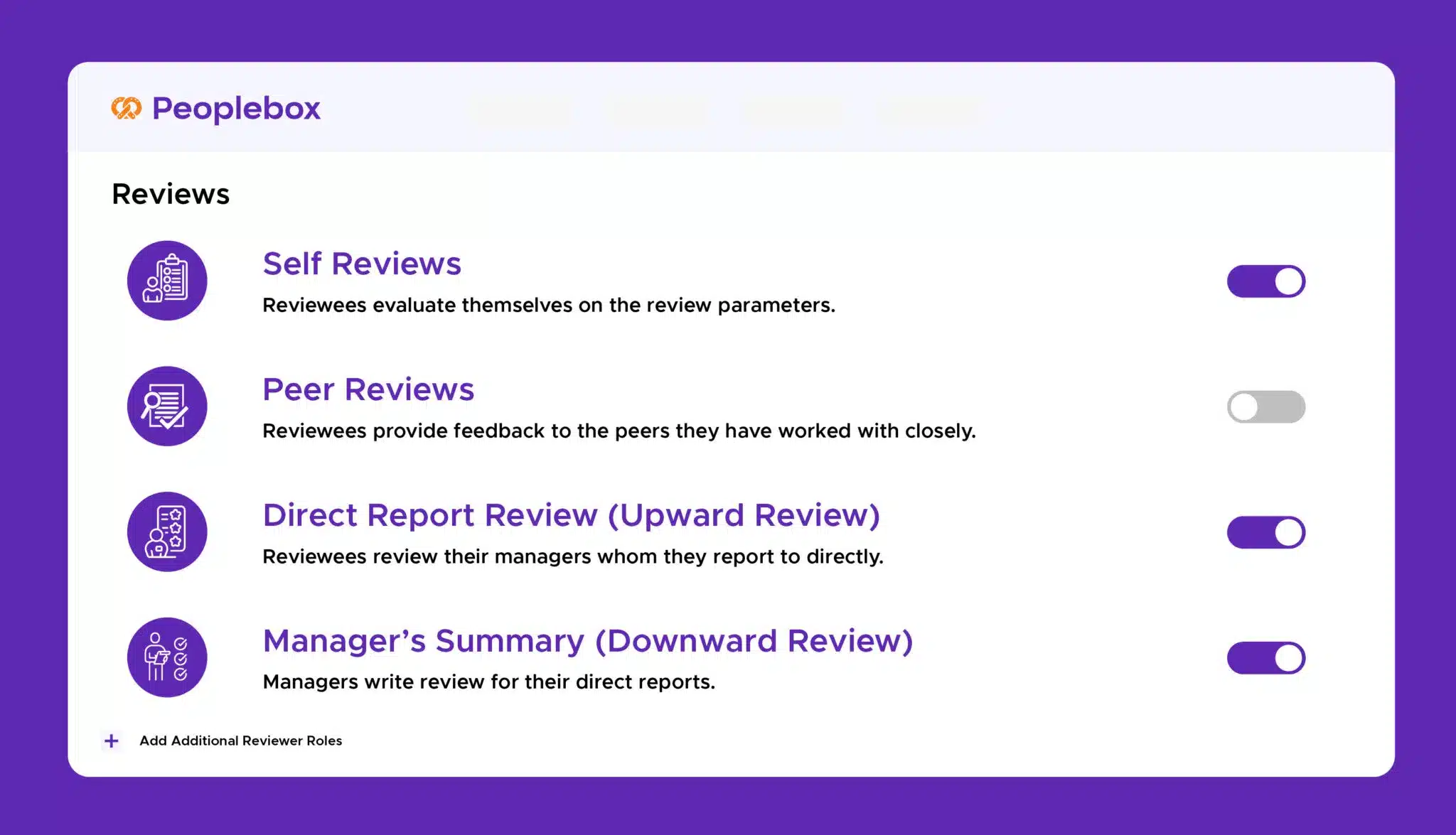
Encouragement of Self-Evaluation
Encourage employees to assess their own performance through Self-Evaluation , fostering self-awareness and continuous improvement.
Structured Assessments
Utilize OKR-based and competency-based evaluations for fair, consistent performance reviews.
Real Time Feedback
Promote ongoing feedback and coaching beyond formal reviews to address issues promptly and support development.
One-on-One Conversations
Schedule and conduct in-depth meetings with employees to discuss performance, career goals, and personalized objectives.
Additionally, Peoplebox.ai offers analytics and reporting functionalities that provide insights into performance trends, employee engagement levels, and areas for organizational improvement. By leveraging these insights, organizations can make data-driven decisions to enhance effective performance management strategies and drive business success.
And the list doesn’t end there! Want to see how you can leverage the Peoplebox.ai performance management platform in your organization? Contact us today!







